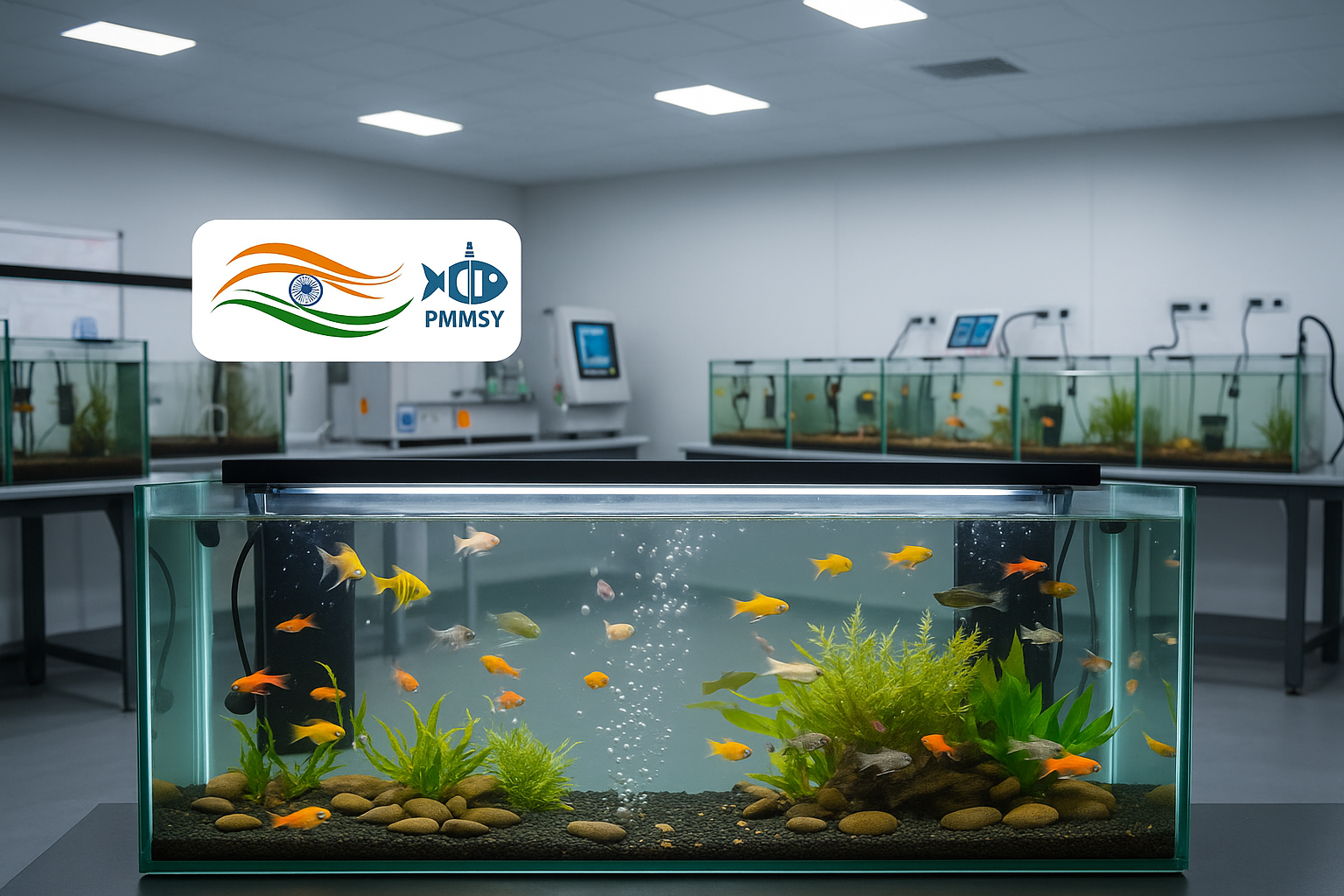
A comprehensive roadmap for aspiring entrepreneurs to establish a profitable freshwater ornamental fish business with government subsidy
Introduction: The Blue Revolution Comes to Your Doorstep
India’s ornamental fish industry stands at a crossroads of tremendous opportunity. While the global market thrives, India’s share remains surprisingly small—a gap that the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) aims to bridge. For entrepreneurs in Haryana, particularly those near the Delhi NCR region, this represents a golden opportunity to enter a growing market with substantial government backing.
The PMMSY, launched with an unprecedented investment of ₹20,050 crores over five years (2020-21 to 2024-25), offers up to 60% subsidy for establishing ornamental fish rearing units. This isn’t just another government scheme—it’s a carefully designed initiative to transform India’s fisheries landscape while creating sustainable livelihoods.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about establishing a medium scale freshwater ornamental fish rearing unit in Haryana, from understanding the subsidy structure to managing daily operations.
Understanding PMMSY: More Than Just a Subsidy Scheme
The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana represents the government’s most comprehensive approach to fisheries development. Its vision extends beyond mere financial assistance:
“Ecologically healthy, economically viable and socially inclusive fisheries sector that contributes towards economic prosperity and well-being of fishers, and fish farmers and other stakeholders, food and nutritional security of the country in a sustainable and responsible manner”
Why Focus on Ornamental Fisheries?
The scheme specifically prioritizes ornamental fisheries because:
- Untapped Export Potential: India holds a negligible share of the $15 billion global ornamental fish trade
- High Returns: Ornamental fish farming offers better profit margins than food fish
- Urban Market Growth: Rising disposable incomes fuel the aquarium hobby
- Employment Generation: Creates opportunities for educated youth
- Low Land Requirement: Suitable for small landholders and urban areas
The Haryana Advantage
Haryana presents unique advantages for ornamental fish farming:
- Market Proximity: Direct access to Delhi NCR’s massive consumer market
- Infrastructure: Well-developed road networks for transportation
- Water Availability: Groundwater and canal networks in most districts
- Climate: Controlled environment farming possible year-round
- Support System: Established fisheries department infrastructure
Decoding the Medium Scale Unit: What Exactly Are You Building?
A medium scale ornamental fish rearing unit under PMMSY is a carefully defined enterprise with specific parameters:
Technical Definition
- Total Project Cost: ₹8,00,000
- Minimum Land Area: 150 square meters (approximately 1,614 sq ft)
- Infrastructure Type: Shed with breeding, rearing, and culture tanks
- Production Capacity: 30,000-40,000 fish annually (after stabilization)
- Unit Classification: Between backyard (₹3 lakh) and integrated (₹25 lakh) units
Physical Infrastructure
Your unit will comprise:
1. Covered Shed Structure (150 sq m) The shed protects your operation from Haryana’s extreme weather—scorching summers and cold winters. Construction typically uses:
- RCC pillars for structural support
- GI sheet or asbestos roofing
- Proper ventilation systems
- Concrete flooring with drainage
2. Tank System (25-30 tanks total)
The tank configuration follows a logical production flow:
- Breeding Tanks (4-6 units): 500-1,000 liter capacity for maintaining broodstock and controlled breeding
- Nursery Tanks (8-12 units): 300-500 liters for fry rearing
- Grow-out Tanks (10-15 units): 200-1,000 liters for raising fish to marketable size
3. Water Management Infrastructure
Critical for maintaining fish health:
- Overhead tank (2,000-5,000 liters)
- Mechanical filtration system
- Biological filtration
- Continuous aeration setup
- Water quality testing equipment
4. Support Facilities
- Small laboratory for water testing
- Feed storage area (dry, rodent-proof)
- Equipment storage
- Packing and dispatch section
- Basic office space for records
What Makes This Scale “Medium”?
The classification isn’t arbitrary. A medium scale unit:
- Manageable by 1-2 persons: Not too large to become unmanageable
- Financially accessible: Total investment under ₹10 lakhs
- Scalable: Room to grow based on success
- Diversifiable: Can handle 5-7 different species
- Commercially viable: Generates meaningful income (₹4-8 lakhs annually after stabilization)
The Money Matter: Complete Financial Breakdown
Understanding the finances is crucial. Let’s break down every rupee.
Total Investment Structure: ₹8,00,000
Civil Construction (52.5% – ₹4,20,000)
| Item | Cost (₹) | Details |
| Shed construction | 2,00,000 | 150 sq m covered area, pillars, roofing, flooring |
| Tank construction | 1,50,000 | Cement/FRP tanks, waterproofing, curing |
| Plumbing system | 40,000 | Inlet/outlet pipes, drainage, connections |
| Electrical installation | 30,000 | Wiring, distribution board, fittings, earthing |
Equipment & Machinery (32.5% – ₹2,60,000)
| Item | Cost (₹) | Purpose |
| Aeration system | 80,000 | Air compressors, airlines, stones |
| Filtration setup | 60,000 | Mechanical and biological filters |
| Water pumps & tanks | 40,000 | Overhead tanks, circulation pumps |
| Climate control | 50,000 | Heaters for winter, cooling for summer |
| Tools & accessories | 30,000 | Nets, siphons, equipment |
Initial Operational Capital (15% – ₹1,20,000)
| Item | Cost (₹) | Details |
| Broodstock | 40,000 | Quality breeding stock for 5-6 species |
| Feed & chemicals | 30,000 | 3 months initial supply |
| Testing equipment | 20,000 | Water quality kits, thermometers |
| Miscellaneous | 30,000 | Licenses, documentation, contingency |
The Subsidy Component: Who Gets What?
This is where PMMSY becomes truly attractive. The government doesn’t just support—it substantially funds your venture.
For General Category Beneficiaries
Government provides 40% of project cost
- Total Project Cost: ₹8,00,000
- Government Assistance: ₹3,20,000
- Central Government share: ₹1,92,000 (60% of govt assistance)
- Haryana State share: ₹1,28,000 (40% of govt assistance)
- Your Contribution: ₹4,80,000 (60%)
Your effective investment: ₹4.80 lakhs for an ₹8 lakh infrastructure
For SC/ST/Women Category
Government provides 60% of project cost
- Total Project Cost: ₹8,00,000
- Government Assistance: ₹4,80,000
- Central Government share: ₹2,88,000
- Haryana State share: ₹1,92,000
- Your Contribution: ₹3,20,000 (40%)
Your effective investment: ₹3.20 lakhs for an ₹8 lakh infrastructure
Financing Your Share
You have three options for your contribution:
1. Own Funds: Use savings or family support
2. Bank Loan: Most common approach
- Banks readily provide loans for PMMSY projects
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme available
- Interest subvention possible
- Typical tenure: 3-5 years
- Need to submit bank sanction letter with application
3. Mixed Approach: Part own funds, part loan
Annual Operating Expenses
Beyond initial investment, plan for recurring costs:
Annual Operating Expenses – Ornamental Fish Unit
| Expense Category | Annual Cost (₹) |
|---|---|
| Fish feed | 1,50,000 – 2,00,000 |
| Electricity | 60,000 – 80,000 |
| Water charges | 20,000 – 30,000 |
| Labor (1-2 persons) | 1,80,000 – 3,60,000 |
| Maintenance & repairs | 40,000 – 60,000 |
| Medicines & chemicals | 30,000 – 50,000 |
| Transportation | 40,000 – 60,000 |
| Miscellaneous | 30,000 – 50,000 |
| Total Annual Operating Expenses | 5,50,000 – 8,90,000 |
Revenue Projections: What Can You Really Earn?
Realistic, not optimistic projections:
Year 1 (Establishment Phase)
- Gross Revenue: ₹4,00,000 – 6,00,000
- Operating Expenses: ₹5,50,000
- Net Profit: ₹1,00,000 – 2,00,000 (25-30% margin)
- Status: Learning phase, building stock
Year 2 (Growth Phase)
- Gross Revenue: ₹8,00,000 – 12,00,000
- Operating Expenses: ₹6,50,000
- Net Profit: ₹3,00,000 – 5,00,000 (35-40% margin)
- Status: Full production capacity reached
Year 3 Onwards (Mature Operations)
- Gross Revenue: ₹12,00,000 – 18,00,000
- Operating Expenses: ₹7,00,000
- Net Profit: ₹5,00,000 – 8,00,000 (40-45% margin)
- Status: Optimized operations, diversified species
Break-Even Analysis
When will you recover your investment?
Assuming:
- Net investment after subsidy (General): ₹4,80,000
- Average annual profit after Year 2: ₹4,00,000
- Loan EMI (if applicable): ₹1,50,000/year
Break-even period: 18-24 months from full production start
This is realistic for a well-managed unit with good market access in Haryana’s NCR region.
Eligibility: Can You Apply?
PMMSY has inclusive eligibility criteria, but specific requirements must be met.
Who Can Apply?
Individual Beneficiaries:
- Fishers (marine or inland)
- Fish farmers
- Entrepreneurs
- Educated unemployed youth
- SC/ST individuals
- Women
Group Entities:
- Self Help Groups (SHGs)
- Joint Liability Groups (JLGs)
- Fisheries Cooperatives
- Fish Farmers Producer Organizations (FFPOs)
Mandatory Requirements
1. Land Requirement
You must have either:
Option A: Owned Land
- Minimum 150 square meters
- Clear title deed
- Free from legal disputes
- Mutation records updated
Option B: Leased Land
- Minimum 150 square meters
- Lease period: Minimum 7 years from application date
- Must be registered lease deed
- Landlord’s written consent
- NOC for construction activities
Critical: The 7-year requirement is firm. Shorter leases won’t be approved.
2. Water Availability
- Reliable water source throughout the year
- Quality suitable for ornamental fish (pH 6.5-7.5)
- Legal rights to water usage
- Sufficient quantity (500-1,000 liters daily)
3. Financial Capacity
You must demonstrate ability to contribute your share through:
- Bank loan sanction letter, OR
- Self-declaration of investment capacity
- Income proof (if applicable)
4. No Dual Subsidy
Critical undertaking: You haven’t received subsidy for same activity under any other government scheme. This is strictly verified.
Unit Allocation Limits
For Individual Beneficiaries:
- Maximum: 1 medium scale unit
For Groups/Cooperatives:
- 1 unit per member
- Maximum: 20 units per group
For FFPOs:
- As decided by Central Apex Committee based on business plan
Preference Categories
While not mandatory, preference given to:
- Fisheries/Zoology/Marine Biology graduates
- Those with prior aquaculture experience
- SC/ST candidates (mandatory quota)
- Women entrepreneurs
- Educated unemployed youth
The Application Journey: Step-by-Step Process
The application process follows a structured timeline. Understanding this helps you plan better.
The Annual Cycle
PMMSY follows an annual planning and approval cycle:
| Month | Activity | Authority |
| October | Tentative allocation to states | DoF, Government of India |
| November | District plans prepared | District Level Committees |
| December | State plan consolidation & approval | SLAMC, Haryana |
| February | National plan approval | Central Apex Committee |
| March 15 | Final allocation communicated | DoF to States |
| April end | Applications submitted to NFDB | State Fisheries Dept |
| May 15 | Appraisal completed | PAC, NFDB |
| May end | Final approval & sanction | DoF, Government of India |
Key Insight: Applications submitted in April-May have best chance of approval in the same financial year.
Your Application Roadmap
Phase 1: Preparation (2-3 months before application)
Step 1: Information Gathering
- Attend district awareness programs
- Visit District Fisheries Office
- Meet existing ornamental fish farmers
- Understand market demand in your area
Step 2: Site Finalization
- Identify suitable location
- Check water source
- Verify electricity availability
- Ensure road access
Step 3: Arrange Finances
- Assess your contribution capacity
- Approach banks for loan (if needed)
- Gather financial documents
Step 4: Document Collection
- Gather all land papers
- Obtain caste certificate (if applicable)
- Get bank statements
- Prepare identity proofs
Phase 2: Proposal Preparation (1 month)
Step 5: Prepare Self-Contained Proposal (SCP)
Your SCP must include:
A. Technical Section
- Site location with GPS coordinates
- Layout plan (drawn to scale)
- Tank specifications and numbers
- Water source details
- Species selection with rationale
- Production methodology
- Timeline for implementation
B. Financial Section
- Detailed cost estimates (component-wise)
- Based on Haryana SoRs and market rates
- Source of beneficiary contribution
- Expected revenue model
- Break-even analysis
C. Documentary Evidence
- Land ownership/lease documents
- Water availability certificate
- Electrical connection proof
- Bank loan sanction (if applicable)
- Identity and category certificates
D. Declarations & Undertakings
- No dual subsidy undertaking
- Land free from encumbrances certificate
- 5-year operation commitment
- Compliance with monitoring
Use Format at Annexure-XI of PMMSY guidelines.
Phase 3: Submission (April)
Step 6: Submit Application
Where: District Fisheries Office, your district
What to carry:
- SCP with all attachments (3 copies)
- All original documents for verification
- Self-attested photocopies
- Application fee (if applicable)
Whom to meet: District Fisheries Officer or designated nodal officer
Get acknowledgement with application number for tracking.
Phase 4: Processing (May-June)
Step 7: District Level Scrutiny
District Level Committee (DLC) headed by District Collector will:
- Verify all documents
- Conduct site inspection
- Interview you (possibly)
- Assess technical feasibility
- Check eligibility
- Approve or reject
Timeline: 15-30 days
Your role: Be available for site visit, answer queries promptly
Step 8: State Level Approval
State Level Approval and Monitoring Committee (SLAMC) headed by Secretary (Fisheries), Haryana will:
- Review all district proposals
- Prioritize based on merit and allocation
- Approve viable projects
- Forward to NFDB
Timeline: As per state schedule
Step 9: National Appraisal
Project Appraisal Committee (PAC) at NFDB will:
- Examine technical viability
- Verify cost reasonableness
- Ensure guideline compliance
- Recommend to DoF
Timeline: 15-20 days
Step 10: Final Approval
Department of Fisheries, Government of India will:
- Issue sanction order
- Specify terms and conditions
- Communicate fund release schedule
Phase 5: Implementation (After Approval)
Step 11: Fund Release
First Installment (typically 50-60%):
- Released after sanction
- Direct to your bank account
- Or through state implementing agency
Step 12: Project Implementation
Start construction as per approved plan:
- Complete within specified timeline (usually 12-18 months)
- Follow approved design
- Maintain quality standards
- Keep all bills and vouchers
Step 13: Progress Monitoring
- Submit quarterly progress reports
- Allow inspection visits
- Maintain photo documentation
- Keep expenditure records
Step 14: Second Installment Release
After 60-70% work completion:
- Submit Utilization Certificate (UC) for first installment
- Show physical progress
- Proof of proportionate beneficiary contribution
- Verification by officials
- Second installment released
Step 15: Project Completion
- Final inspection
- Completion certificate issued
- Begin operations
- Submit final UC
Common Application Mistakes to Avoid
- Incomplete documentation: Single most common rejection reason
- Unrealistic cost estimates: Either too high or too low
- Short lease period: Less than 7 years not accepted
- Poor site selection: Water unavailability, access issues
- Dual subsidy: Applying under multiple schemes
- Missing undertakings: Forgetting mandatory declarations
- Late submission: Missing the annual cycle
- Poor SCP preparation: Lack of technical details
Setting Up Your Unit: From Approval to Operations
Once your project has received approval, the next stage is implementation. This stage is crucial because it transforms the approved plan into a fully functional unit. On average, the complete process takes 12–16 weeks. Each phase builds upon the previous one, moving systematically from site preparation to full operationalization of the unit.
Weeks 1–2: Site Preparation
The first step is preparing the site, which serves as the foundation for all further work. During this period, the land is cleared of debris and leveled to ensure stability for construction. A temporary storage shed is set up on-site to safely house raw materials, tools, and equipment as they are delivered.
Material procurement begins early to avoid delays later in construction. At the same time, an application for a new electricity connection should be made (if one does not already exist), since reliable power will be essential for equipment operation. This stage also involves hiring laborers or finalizing contracts with civil contractors.
By the end of the second week, the site should be neat, organized, and fully ready to begin construction. The cost of this phase is generally already included in the approved project budget.
Weeks 3–8: Civil Construction
Civil construction is the most time-intensive phase, spanning about six weeks. It is carried out in three sub-stages: foundation and structure, roofing and walls, and finally, tank construction.
Foundation & Structure (Weeks 3–4):
Construction begins by marking the layout of the unit as per the approved plan. Excavation work is carried out for laying the foundations of pillars and tanks. Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) pillars are cast, and foundations for tanks are constructed. Adequate curing time is allowed to ensure strength and durability.
Roofing & Walls (Weeks 5–6):
Once the foundation is secure, roofing work begins. Roof trusses are erected and GI sheets are fitted to provide cover. Side walls or curtain systems are built to enclose the facility while maintaining proper ventilation openings.
Tank Construction (Weeks 7–8):
The tanks, which form the heart of the unit, are constructed next. Depending on the project design, either cement tanks are built or FRP/readymade tanks are installed. All tanks are thoroughly waterproofed, and inlet/outlet fittings are fixed. For cement tanks, additional curing time is required to prevent leakage or cracks.
Parallel Work:
While these main activities take place, plumbing, drainage, and electrical conduit laying are carried out in parallel. Special care is taken to maintain proper slope in drainage lines to prevent waterlogging.
Quality Checks:
Before moving to the next stage, a series of quality checks are essential. These include verifying waterproofing quality, ensuring the roof is leak-proof, checking the slope of drainage lines, and performing tank leak tests.
Weeks 9–10: Equipment Installation
With civil works complete, attention shifts to installing key equipment and utilities.
Electrical Setup:
The electrical system is finalized by installing the distribution board, completing wiring, and fixing light fittings and sockets. Safety features such as proper earthing are put in place to ensure smooth and hazard-free operation.
Water System:
Water is the lifeline of the unit, so an overhead tank is installed to maintain water pressure. Pumps and filtration systems are mounted, and the pipeline network is connected across the tanks.
Aeration System:
To maintain dissolved oxygen levels, air compressors are installed and connected through an airline network. Air stones are distributed evenly in tanks, followed by test runs to confirm adequate oxygen flow.
Climate Control:
Depending on local climatic conditions, heaters or cooling systems are set up. Thermometers are placed at strategic points for temperature monitoring.
By the end of this stage, the physical infrastructure of the unit is complete, with all mechanical and electrical systems in place.
Weeks 11–12: Testing & Commissioning
Before live operations begin, all systems undergo rigorous testing.
The tanks are filled with water, and every piece of equipment—pumps, filters, aerators, and electrical fittings—is run continuously for at least 48 hours. During this period, leaks, short circuits, or mechanical faults are carefully checked and rectified. Backup power arrangements are also tested.
Next comes bio-cycling, a critical step to prepare tanks for aquatic life. Beneficial bacteria are added, and the filtration system is run continuously. Ammonia and nitrite levels are monitored until they drop to zero, which usually takes 2–3 weeks. This ensures a safe and healthy aquatic environment.
As the unit nears readiness, final touches are completed. These include installing a signboard acknowledging PMMSY support, fencing the boundary, landscaping, constructing access roads, and arranging security measures.
Weeks 13–14: Broodstock Introduction
Once the tanks are stable, broodstock introduction begins.
Broodstock is sourced from certified suppliers, preferably government hatcheries, to ensure quality and genetic purity. Each batch is accompanied by valid health certificates and is transported in oxygenated bags to maintain vitality during transit.
Upon arrival, the broodstock is kept in a separate quarantine tank for 14 days. This period is used to observe for signs of disease, administer preventive treatments if necessary, and gradually acclimatize the stock to the new environment.
After successful quarantine, the broodstock is transferred to breeding tanks. Hardy species are introduced first, and their behavior and feeding response are closely monitored. A structured feeding protocol is initiated at this stage.
Weeks 15–16: Full Operationalization
By this time, the unit is fully functional. All planned species are introduced into their respective tanks, feeding routines are established, and daily monitoring begins. Record-keeping systems are put in place to track water quality, feeding schedules, health status, and breeding activity.
The first breeding attempts are usually initiated during this phase, officially marking the transition of the unit from a construction site to a fully operational production facility.
Species Selection: Building Your Product Portfolio
Choosing the right species determines your success. For Haryana conditions, consider these factors:
Criteria for Species Selection
- Market Demand: What sells in your target market?
- Breeding Ease: How quickly can you produce?
- Haryana Climate: Temperature tolerance
- Space Requirements: Tank space vs. returns
- Skill Level: Your experience
- Price Point: Profit margins
Recommended Species Portfolio for Haryana
Tier 1: Foundation Species (50% of production)
1. Goldfish (Carassius auratus)
Why perfect for Haryana:
- Cold tolerant (15-25°C) – survives Haryana winters
- Extremely high demand
- Multiple varieties from single species
- Long lifespan increases repeat sales
Varieties to breed:
- Common Goldfish: ₹10-20 (high volume)
- Comet: ₹30-50
- Fantail: ₹50-100
- Oranda: ₹100-300
- Ranchu: ₹150-500
Breeding:
- Spawning: Spring (February-March) ideal
- Fry per female: 1,000-2,000
- Marketable size: 3-4 months
- Expected annual production: 6,000-8,000 fish
2. Guppy (Poecilia reticulata)
Why essential:
- Livebearer – easiest breeding
- 30-day reproduction cycle
- Consistent year-round production
- Low maintenance
Economics:
- Price: ₹5-15 per fish
- Volume compensates for lower price
- Expected annual production: 15,000-20,000 fish
Breeding advantage:
- No egg care needed
- Fry born swimming
- Multiple strains possible
Tier 2: Value Species (30% of production)
3. Molly & Platy (Poecilia/Xiphophorus spp.)
Market positioning:
- Mid-price range
- Reliable sellers
- Hardy and adaptable
Varieties:
- Black Molly: ₹15-30
- Dalmatian Molly: ₹20-40
- Platy (assorted): ₹15-25
Production:
- Similar to Guppies (livebearing)
- Slightly larger size
- Expected annual production: 8,000-10,000 fish
4. Angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare)
Premium positioning:
- Higher price point (₹30-300)
- Strong demand
- Multiple color varieties
Breeding considerations:
- Requires more skill
- Egg-laying species
- Parental care interesting to observe
- Expected annual production: 2,000-3,000 fish
Tier 3: Premium Species (20% of production)
5. Fighter Fish/Betta (Betta splendens)
Why lucrative:
- High price: ₹50-500 per fish
- Display/pet fish market
- Individual selling possible
Special requirements:
- Males must be separated
- More space per fish
- Selective breeding for colors
- Expected annual production: 1,000-1,500 fish
6. Swordtails (Xiphophorus hellerii)
Market appeal:
- Distinctive tail
- Hardy nature
- Good community fish
- Price: ₹15-80
Production: Similar to Mollies/Platies
Species You Should Avoid Initially
While tempting, avoid these until experienced:
- Discus: Requires precise water parameters
- Arowana: Very high investment, difficult breeding
- Marine species: Different infrastructure needed
- Exotic rarities: Limited market in Haryana
Seasonal Production Strategy
Winter (November-February):
- Focus on cold-tolerant: Goldfish, Platies
- Reduce breeding of tropical species
- Maintain broodstock only
- Prepare for spring breeding
Spring (March-May):
- Peak breeding season
- Maximum production
- All species active
- Build inventory for summer sales
Summer (June-August):
- Controlled environment crucial
- Continue breeding with cooling
- Higher mortality risk – be cautious
- Focus on hardy species
Monsoon & Post-Monsoon (September-October):
- Excellent growing conditions
- Prepare stock for festival season
- Diwali demand peak
- Build inventory for winter
Stocking Density Guidelines
Avoid overcrowding – single biggest mistake:
| Life Stage | Density | Tank Size |
| Fry (0-2 weeks) | 500-1,000/tank | 300-500 L |
| Juveniles (2-8 weeks) | 200-300/tank | 500 L |
| Sub-adults | 100-150/tank | 500-1,000 L |
| Adults | 50-100/tank | 1,000 L |
| Broodstock | 20-30 pairs/tank | 1,000 L |
Remember: These are maximums. Lower density = healthier fish.
Detailed Explanation of Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Operations
The daily routine is the bedrock of a healthy and productive unit, designed to ensure continuous environmental stability and rapid response to issues.
The daily schedule is focused on stability, observation, and immediate action.
- Morning Shift (7:00 AM – 10:00 AM): Focus is on proactive setup. This includes the critical Health Check (looking for signs of disease/stress), a small First Feeding (30% ration), and the System Check to confirm all aeration and filtration are operational. Also includes initial cleaning and Breeding Management (collecting eggs/fry).
- Afternoon Shift (2:00 PM – 4:00 PM): Focus is on quality control and growth. This features the Second Feeding (the main 40% meal), mandatory Water Quality Testing (pH, Ammonia, Nitrite), and Grading & Sorting fish by size to maximize growth and prevent cannibalism.
- Evening Shift (6:00 PM – 7:00 PM): Focus is on secure wind-down. This involves the Final Feeding (light 30% ration), a Final Inspection of all systems for the overnight period, and Record Keeping to log the day’s events.
Weekly Tasks: System Maintenance and Optimization
Weekly tasks are for preventive maintenance and strategic planning, ensuring long-term health and efficiency.
- Water Changes (Monday): Removes nitrates and replenishes minerals (20-30%).
- Filter Maintenance (Tuesday): Cleans mechanical filters while preserving the vital biological filter (rinse with tank water only!).
- Stock Taking (Wednesday): Updates inventory and calculates growth rates (key performance indicator).
- Equipment Check (Thursday): Tests backup power and inspects equipment for wear/tear to prevent costly failures.
- Quality Control (Friday): Culls defective fish and selects the best specimens for breeding to improve genetic quality.
- Deep Cleaning & Planning (Sat/Sun): Thoroughly sanitizes nets/tanks and handles administrative/marketing tasks.
Monthly Operations: Strategic Oversight
Monthly tasks address high-level financial, health, and equipment longevity needs.
- Health Management: Comprehensive inspection, deworming, and strict quarantine of new stock to prevent disease.
- Financial Accounting: Updates profit/loss statements and budgets for strategic decision-making.
- Equipment Maintenance: Servicing air compressors and calibrating test equipment for accuracy.
Feeding Management Summary
- Rule: Feed high-quality rations only what the fish consume in 5 minutes.
- Frequency: Increases with metabolic rate (e.g., 6-8 times/day for fry, 2-3 times/day for broodstock).
- Safety: Never overfeed, and do not feed if water quality (Ammonia/Nitrite) is poor.
- Variety: Vary the diet (dry, live, frozen) for complete nutrition and health.
Record Keeping System
Maintain these registers religiously:
1. Daily Stock Register:
Date | Tank No | Species | Count | Size | Health Status | Action Taken
2. Water Quality Log:
Date | Tank No | Temp | pH | NH3 | NO2 | DO | Action
3. Breeding Record:
Date | Species | Male ID | Female ID | Eggs/Fry | Hatch Rate | Remarks
4. Mortality Register:
Date | Tank No | Species | Count | Size | Suspected Cause | Prevention
5. Sales Ledger:
Date | Buyer | Species | Quantity | Rate | Amount | Payment Status
6. Expense Book:
Date | Category | Item | Quantity | Rate | Amount | Bill No
7. Feed Consumption:
Date | Feed Type | Quantity Used | Cost | Tanks Fed | Remarks
These records are mandatory for:
- Monitoring visits
- Problem diagnosis
- Financial planning
- Loan documentation
- Insurance claims
Marketing: Turning Fish Into Revenue
Primary Market (60-70% sales): Delhi NCR Region
- Ghazipur Fish Market (wholesale)
- Local aquarium shops (retail)
- Pet stores in malls
- Online platforms
Secondary Market (20-30% sales): Punjab, Chandigarh
- Wholesale dealers
- Established retail chains
Tertiary Market (10-20% sales): Haryana Cities
- Gurgaon, Faridabad urban centers
- Growing middle-class aquarium enthusiasts
- Corporate offices (aquarium installations)
Emerging Market: Export (long-term goal)
- Requires MPEDA certification
- International quality standards
- Higher prices but complex logistics
Pricing Strategy
Farm Gate Pricing (Your Selling Price):
Ornamental Fish Pricing – Wholesale vs Retail
| Species | Size | Your Price (₹) | Retail Price (₹) | Your Margin (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guppy | Adult | ₹8-12 | ₹20-40 | ₹6-10 |
| Molly | Adult | ₹15-25 | ₹40-80 | ₹12-20 |
| Platy | Adult | ₹12-20 | ₹30-60 | ₹10-15 |
| Goldfish (Common) | 2-3 inch | ₹15-25 | ₹40-80 | ₹12-20 |
| Goldfish (Fancy) | 2-3 inch | ₹40-80 | ₹100-200 | ₹35-65 |
| Angelfish | 2 inch | ₹40-60 | ₹100-150 | ₹35-50 |
| Fighter Fish | Adult male | ₹80-150 | ₹200-400 | ₹70-130 |
Volume Discounts:
- 100+ pieces: 10% discount
- 500+ pieces: 15% discount
- 1000+ pieces: 20% discount
Seasonal Pricing:
- Festival season (Diwali, New Year): +20-30%
- Wedding season (November-February): +15-20%
- Monsoon slow period: Maintain base price
Sales Channels
Channel 1: Direct to Retail Shops
Process:
- Identify 10-15 aquarium shops within 50 km
- Visit with samples
- Offer credit period (15-30 days)
- Weekly/bi-weekly supply schedule
- Take back dead fish policy (7 days)
Advantages:
- Better margins (15-20% more than wholesale)
- Direct customer feedback
- Relationship building
Requirements:
- Reliable transport
- Quality consistency
- Quick response to orders
Channel 2: Wholesale Markets
Primary Hub: Ghazipur Fish Market, Delhi
- Timings: 5 AM – 10 AM
- Peak days: Thursday-Saturday
- Payment: Mostly cash, same day
Process:
- Reach by 5-6 AM
- Display your fish
- Negotiate with wholesalers
- Sell in bulk
- Return by noon
Advantages:
- Bulk clearance
- Immediate payment
- No credit risk
Disadvantages:
- Lower prices (20-30% less than retail)
- Early morning travel
- Price negotiation pressure
Channel 3: Online Sales
Platforms:
- OLX, Quikr (free listings)
- Facebook Marketplace
- Instagram Business Page
- WhatsApp Business
- Dedicated website (later stage)
Strategy:
- Professional photography
- Species information posts
- Care tips content
- Customer testimonials
- Local delivery offers
Pricing: Higher margins possible (retail equivalent)
Challenges:
- Logistics for live fish
- Return/replacement requests
- Customer education needed
Channel 4: Corporate & Event Sales
Target Customers:
- Corporate offices (reception aquariums)
- Restaurants and hotels
- Wedding decorators
- Event management companies
Offering:
- Bulk supply for events
- Aquarium setup services
- Maintenance contracts
- Consultation fees
Margins: 30-40% higher than retail
Marketing Activities
Month 1-3: Foundation Building
Activities:
- Create business cards (₹2,000)
- Install signboard at unit (₹5,000)
- Register on Google My Business (Free)
- Create WhatsApp Business account (Free)
- Join local aquarium groups (Free)
Goal: Establish presence, first 5 customers
Month 4-6: Active Promotion
Activities:
- Visit 20 retail shops with samples
- Supply to 3-5 regular customers
- Attend Ghazipur market twice
- Create Instagram page with 50 posts
- Print brochures (₹5,000 for 1,000 copies)
Goal: ₹50,000/month sales
Month 7-12: Expansion
Activities:
- Participate in aquarium exhibition (Delhi/Gurgaon)
- Conduct school awareness program
- Launch fish care YouTube channel
- Tie-up with 10+ retail shops
- Start corporate outreach
Goal: ₹1,00,000/month sales
Year 2 Onwards: Diversification
Activities:
- Export registration (MPEDA)
- Premium species introduction
- Value-added services (aquarium setup)
- Training workshops (paid)
- Franchise model exploration
Building Your Brand
Brand Name Selection:
- Should reflect fish/water theme
- Easy to remember
- Available as domain name
Examples:
- “AquaBloom Farms”
- “Rainbow Fish Hatchery”
- “Crystal Waters Ornamentals”
- “[Your Name] Aqua World”
Brand Identity:
- Logo design (₹5,000-10,000)
- Color scheme (blues, greens)
- Tagline: “Quality Fish, Healthy Life”
- PMMSY beneficiary badge display
Quality Markers:
- “Government Certified Unit”
- “PMMSY Supported Enterprise”
- “Quarantined & Health-Tested”
- “7-Day Guarantee”
Customer Retention
After-Sales Support:
- Fish care instruction sheet with every sale
- WhatsApp helpline for queries
- Emergency consultation (free for 30 days)
- Replacement for genuine health issues
Loyalty Program:
- Repeat customer discount: 5%
- Referral bonus: ₹100-500
- Festival special offers
- Birthday month discount
Customer Education:
- Monthly newsletter (via WhatsApp)
- Fish care videos
- Common problem solutions
- Feeding guidelines
- Tank maintenance tips
Handling Competition
Your Competitive Advantages:
- Government certification: PMMSY beneficiary status
- Quality focus: Better survival rates
- Service orientation: Education and support
- Local presence: Quick delivery
- Variety: 5-7 species from one source
Dealing with Price Competition:
- Don’t compete on price alone
- Emphasize quality and service
- Offer value-adds (free advice, guarantees)
- Build relationships, not transactions
Sales Projections (Realistic)
Year 1 Monthly Progression:
Monthly Sales and Distribution Channels
| Month | Sales (₹) | Primary Channel |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 10,000 – 20,000 | Friends, local shops |
| 4-6 | 30,000 – 50,000 | Retail shops (5-7) |
| 7-9 | 50,000 – 80,000 | Wholesale + retail |
| 10-12 | 80,000 – 1,00,000 | Multiple channels |
Year 2 Onwards:
- Average monthly sales: ₹1,00,000-1,50,000
- Peak months (festivals): ₹2,00,000+
- Low months (monsoon): ₹80,000
Common Challenges and Solutions
Every business faces challenges. Here’s how to handle ornamental fish farming issues:
Challenge 1: High Initial Mortality (30-50%)
Symptoms:
- Newly stocked fish dying within 48 hours
- Fry mortality in first week
- No obvious disease signs
Root Causes:
- Poor acclimatization
- Sudden water parameter change
- Transport stress
- Weak broodstock
Solutions:
Immediate Actions:
- Stop feeding for 24 hours
- Increase aeration
- Partial water change (20%)
- Add stress coat/salt (as per species)
Preventive Measures:
- Quarantine protocol: 14 days mandatory for new stock
- Gradual acclimatization:
- Float bag for 30 minutes (temperature match)
- Add tank water gradually (pH, TDS match)
- Release after 2 hours
- Source quality: Only certified suppliers
- Transport properly: Oxygen bags, insulated boxes
Challenge 2: Water Quality Crashes
Symptoms:
- Fish gasping at surface
- Ammonia spike
- Cloudy water
- Mass mortality
Root Causes:
- Overfeeding (most common)
- Filter failure
- Power cut (aeration stopped)
- Overcrowding
- Dead fish decomposing
Solutions:
Emergency Protocol:
- Immediate 50% water change
- Stop feeding completely
- Increase aeration to maximum
- Add beneficial bacteria
- Remove all debris/dead fish
- Test water every 6 hours
Prevention:
- Feed discipline: Only what fish consume in 5 minutes
- Daily cleaning: Siphon uneaten food and waste
- Regular testing: At least 3 tanks daily
- Backup power: Mandatory investment
- Stocking density: Don’t exceed recommended limits
Water Quality Targets:
- Ammonia: 0 ppm
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
- Nitrate: <20 ppm
- pH: 6.5-7.5
- Temperature: 24-28°C (species dependent)
Challenge 3: Breeding Failures
Symptoms:
- Fish not spawning
- Eggs not hatching
- Fry not surviving
- Reduced fertility
Root Causes:
- Poor broodstock nutrition
- Incorrect water parameters
- Stress factors
- Genetic issues (inbreeding)
Solutions:
For Egg-layers (Angelfish, etc.):
- Separate breeding tank
- Condition pair with live food (2 weeks)
- Trigger breeding:
- Raise temperature 2°C
- 30% water change with cooler water
- Increase protein in diet
- Provide spawning surface (slate, leaf)
For Livebearers (Guppy, Molly):
- Maintain 3:1 female to male ratio
- Well-fed females
- Separate pregnant females
- Dense plants for fry hiding
Broodstock Management:
- Rotate breeding pairs
- Don’t breed same pair continuously
- Introduce new bloodlines annually
- Cull defective offspring
- Keep breeding records
Challenge 4: Disease Outbreaks
Common Diseases in Haryana Conditions:
1. White Spot (Ich)
- Symptoms: White spots like salt grains
- Cause: Parasite (temperature fluctuation)
- Treatment:
- Raise temperature to 30°C gradually
- Add salt (1 tablespoon per 10 liters)
- Commercial ich medication
- Continue 7 days after spots disappear
2. Fungal Infections
- Symptoms: Cotton-like growth
- Cause: Poor water quality, injury
- Treatment:
- Isolate affected fish
- Antifungal medication (malachite green)
- Improve water quality
- Add salt (stress reducer)
3. Fin Rot
- Symptoms: Frayed, discolored fins
- Cause: Bacterial infection
- Treatment:
- Antibiotic bath
- Improve water quality
- Separate aggressive fish
4. Dropsy
- Symptoms: Swollen belly, raised scales
- Cause: Bacterial, often fatal
- Treatment:
- Isolate immediately
- Antibiotic treatment (limited success)
- Euthanize humanely if suffering
- Disinfect tank
Disease Prevention Strategy:
- Quarantine: All new stock, 14 days minimum
- Biosecurity:
- Separate nets per tank
- Footbath at entry
- Disinfect equipment between tanks
- Water quality: Maintain optimal parameters always
- Nutrition: Quality feed, varied diet
- Stress reduction: No overcrowding, stable conditions
- Regular observation: Catch problems early
Medicine Cabinet Essentials (₹5,000-7,000):
- Potassium permanganate (disinfectant)
- Malachite green (fungal)
- Methylene blue (bacterial)
- Salt (stress, parasites)
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Anti-parasitic medication
Challenge 5: Inconsistent Sales
Symptoms:
- Some months no sales
- Unsold stock accumulating
- Cash flow problems
Root Causes:
- Seasonal demand variations
- Limited buyer network
- Production-demand mismatch
- Competition
Solutions:
Demand Planning:
- Study seasonal patterns
- Plan breeding accordingly
- Build inventory before peak seasons
- Reduce production in slow months
Diversify Buyers:
- Don’t depend on 1-2 customers
- Develop minimum 10 regular buyers
- Mix of retail and wholesale
- Online presence for direct sales
Product Diversification:
- Maintain 5-7 species
- Different price points
- Fast movers (Guppy) + high value (Angelfish)
- Special colors/varieties
Value-Added Services:
- Aquarium setup consultancy
- Maintenance contracts
- Fish food sales
- Accessories retailing
Financial Buffer:
- Keep 3 months operating expense as reserve
- Don’t expand too quickly
- Maintain relationship with bank for working capital
Challenge 6: Power Cuts (Critical in Rural Haryana)
Impact:
- Aeration stops → oxygen depletion
- Fish mortality within 2-4 hours
- Can wipe out entire stock
Solutions:
Mandatory Backup (₹50,000-1,00,000):
- Inverter + batteries (minimum 4-6 hours)
- Or diesel generator
- Or solar power system
- Automatic changeover
Emergency Protocol:
- Manual aeration (pour water from height)
- Reduce feeding
- Remove waste to reduce oxygen demand
- Increase water surface area
- Add hydrogen peroxide (emergency only, 1ml/10L)
Power Cut Prevention:
- Register for priority electricity connection
- Maintain backup system religiously
- Test backup weekly
- Keep diesel/petrol reserve
Challenge 7: Skilled Labor Shortage
Problems:
- Finding trained staff
- High turnover
- Theft/carelessness issues
Solutions:
Hiring Strategy:
- Prefer local youth (less likely to leave)
- Agriculture background helpful
- Willingness to learn > experience
- Start with daily wage, convert to monthly after trial
Training Program:
- Week 1: Observe and learn
- Week 2: Feeding and cleaning under supervision
- Week 3: Independent tank management
- Week 4: Disease identification, breeding basics
- Month 2: Full operations
Retention:
- Competitive wages (₹10,000-15,000/month)
- Performance bonuses
- Festival bonuses
- Respect and recognition
- Growth opportunities
Documentation:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Video documentation of key processes
- Checklists for daily tasks
- Reduces dependency on one person
Challenge 8: Regulatory Compliance
Required Compliances:
- Local business registration
- GST registration (if turnover >₹20 lakhs)
- Environmental clearances (if applicable)
- Trade license from local authority
- Food safety license (for fish food sales)
PMMSY Specific:
- Maintain proper records
- Allow monitoring visits
- Submit quarterly reports
- Display PMMSY beneficiary board
- Don’t divert subsidy
- Maintain operations minimum 5 years
Penalty for Non-Compliance:
- Subsidy recovery with interest
- Penal interest @12% per annum
- Blacklisting from future schemes
Solution: Hire a local CA for basic compliance (₹5,000-10,000/year)
Financial Planning and Management
Initial Capital Requirement Summary
Total Needed to Start (General Category):
Project Financial Components
| Component | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|
| Total project cost | 8,00,000 |
| Less: Government subsidy | (3,20,000) |
| Your contribution needed | 4,80,000 |
| Working capital (3 months) | 1,50,000 |
| Total capital to arrange | 6,30,000 |
How to Arrange:
- Own savings: ₹2,00,000
- Bank loan (against subsidy + property): ₹3,00,000
- Family support: ₹1,30,000
Loan Options
Kisan Credit Card (KCC):
- Available for fisheries
- Up to ₹3 lakhs without collateral
- Interest rate: 4-7% (with subvention)
- Repayment: Flexible, linked to production cycle
Term Loan:
- For larger amounts
- Collateral: Your land or family property
- Interest rate: 8-11%
- Tenure: 5-7 years
NABARD Refinance:
- Through commercial banks
- Special schemes for aquaculture
- Lower interest rates
Bank Approach:
- Prepare solid business plan
- Show PMMSY sanction letter
- Demonstrate own contribution (20-30%)
- Highlight market potential (Delhi NCR)
- Show experience/education
- Clean credit history
Break-Even Analysis Detailed
Assumptions:
- Project cost: ₹8 lakhs
- Your investment (after subsidy): ₹4.8 lakhs (General)
- Bank loan taken: ₹3 lakhs @ 9% interest
- Loan EMI: ₹5,500/month = ₹66,000/year
Fixed Costs (Annual):
- Depreciation: ₹40,000
- Loan EMI: ₹66,000
- Insurance: ₹10,000
- License/compliance: ₹5,000
- Total Fixed: ₹1,21,000
Variable Costs (Annual):
- Feed: ₹1,75,000
- Electricity: ₹70,000
- Labor: ₹2,40,000
- Chemicals/medicines: ₹40,000
- Transport: ₹50,000
- Miscellaneous: ₹40,000
- Total Variable: ₹6,15,000
Total Annual Cost: ₹7,36,000
Revenue Needed to Break Even: ₹7,36,000
At Average Price of ₹25/fish: Need to sell 29,440 fish/year
Your Production Target (Year 2+): 35,000-40,000 fish/year
Break-Even: Achieved in Month 18-20
Profit After Break-Even (Year 2):
- Revenue: ₹11,00,000 (35,000 fish × ₹31 avg)
- Total costs: ₹7,36,000
- Net Profit: ₹3,64,000
Cash Flow Management
Critical Months:
- Months 1-6: Cash outflow (construction, stocking)
- Months 7-12: Starting income, still negative cash flow
- Month 13 onwards: Positive cash flow
Managing Cash Crunch:
- Keep 3-month expense reserve
- Stagger production (rolling batches)
- Mix fast-growing (Guppy-30 days) and slow (Angelfish-120 days)
- Negotiate 30-day credit with feed suppliers
- Get 15-day credit period from retailers
- Emergency line of credit from bank
Profit Reinvestment Strategy:
- Year 1: Survive, stabilize, learn
- Year 2: Repay loan faster (save interest)
- Year 3: Expand (more tanks) or diversify (premium species)
- Year 4-5: Consider second unit or franchise model
Tax Planning
Income Tax:
- Agricultural income generally exempt
- But ornamental fish farming may be considered business
- Consult CA for proper classification
- Maintain proper books
GST:
- Registration mandatory if turnover >₹20 lakhs
- Rate: 0% or 5% (check latest schedule)
- Input tax credit available
Tax Benefits:
- Depreciation on equipment
- Interest deduction on loan
- Business expenses fully deductible
Conclusion: Your Journey Begins Here
Starting a medium scale ornamental fish rearing unit under PMMSY in Haryana is not just a business opportunity—it’s a pathway to sustainable livelihood, entrepreneurship, and contribution to India’s Blue Revolution.
Why This Opportunity is Special
1. Substantial Government Support: 40-60% subsidy significantly reduces your financial burden
2. Growing Market: Delhi NCR’s expanding middle class ensures robust demand
3. Reasonable Investment: At ₹8 lakhs total (₹3-5 lakhs your share), it’s accessible to many
4. Quick Returns: Break-even in 18-24 months, unlike many agricultural ventures
5. Scalable Business: Start medium scale, grow based on success
6. Sustainable Livelihood: ₹5-8 lakhs annual profit after stabilization
7. Government Backing: Technical support, training, and monitoring ensures success
Is This Right for You?
You’re an Ideal Candidate If:
- You have/can arrange ₹3-5 lakhs
- You have minimum 150 sq m land (owned/leased 7+ years)
- You’re willing to work daily (no holidays concept)
- You can handle biological risks (fish mortality)
- You have patience for 18-24 months to profits
- You’re near urban markets (preferably NCR region)
- You’re comfortable with technology and record-keeping
Think Twice If:
- You expect overnight profits
- You can’t arrange ₹3-5 lakhs
- You don’t have time for daily operations
- You’re uncomfortable handling live animals
- You’re far from markets with poor connectivity
- You can’t handle business uncertainties
Your Action Plan (Next 30 Days)
Week 1: Research and Planning
- Download PMMSY guidelines from dof.gov.in
- Visit 2-3 existing ornamental fish units
- Contact District Fisheries Office
- Assess your financial capacity
- Finalize land (owned or lease)
Week 2: Feasibility and Learning
- Attend PMMSY awareness program (if available)
- Join online ornamental fish communities
- Study market (visit Ghazipur if possible)
- Calculate realistic costs for your location
- Identify potential buyers
Week 3: Documentation
- Gather all required documents
- Get land documents verified
- Apply for bank loan (if needed)
- Obtain necessary certificates
- Prepare preliminary project outline
Week 4: Application Preparation
- Draft Self-Contained Proposal
- Prepare detailed cost estimates
- Get estimates from suppliers
- Take site photographs
- Submit application to District Fisheries Office
Final Words of Advice
1. Start Conservative: Don’t be overambitious. Master 3-4 species before diversifying.
2. Quality First: One healthy, beautiful fish sells for more than ten sickly ones. Never compromise on water quality or nutrition.
3. Document Everything: Your records save you during inspections, help diagnose problems, and guide business decisions.
4. Build Relationships: With buyers, suppliers, fellow farmers, and fisheries officers. This business thrives on trust.
5. Continuous Learning: Ornamental fish farming is part science, part art. Every day teaches something new.
6. Patience and Persistence: First year is learning. Second year is establishing. Third year onwards, you reap rewards.
7. Ethics Matter: Treat fish humanely. Sell healthy stock. Be honest with customers. Long-term success comes from integrity.
8. Embrace Technology: Use WhatsApp for orders, maintain digital records, create social media presence. Modern farming needs modern tools.
9. Plan for Emergencies: Power backup isn’t optional. Keep emergency medicines. Have vet contact ready. Fish don’t wait.
10. Enjoy the Journey: There’s something magical about breeding life, seeing colors emerge, creating beauty. Beyond profits, find joy in the craft.
The Bigger Picture
You’re not just starting a business. You’re:
- Contributing to India’s food security and nutrition goals
- Creating employment (direct and indirect)
- Promoting sustainable aquaculture
- Preserving aquatic biodiversity through captive breeding
- Bringing joy to thousands of aquarium enthusiasts
- Setting example for rural entrepreneurship
The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana has opened doors. Now it’s your turn to walk through and create your success story.
Remember: Every successful ornamental fish farmer started exactly where you are today—with a dream, a plan, and the courage to begin.
Appendices
Appendix A: Important Forms and Formats
1. Self-Contained Proposal Format (Use format as provided in PMMSY Annexure-XI)
2. Land Certificate Format (Use format as provided in PMMSY Annexure-XI of operational guidelines
3. Utilization Certificate (Use GFR 12-A or 12-C format as provided in Annexure-XII)
4. Daily Operations Checklist:
I created a visual representation of the Daily Operations Checklist using React on Bolt website. This allows the checklist to be interactive, responsive, and easy to use on any device. Unlike static paper formats, the digital version enables clickable checkboxes, clean layout, and mobile-friendly design, making record-keeping and monitoring more efficient for the ornamental fish unit.
Appendix B: Water Quality Management Guide
Acceptable Ranges for Major Ornamental Fish Species
Acceptable Ranges for Major Ornamental Fish Species
| Parameter | Goldfish | Guppy/Molly | Angelfish | Fighter Fish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 18-25°C | 24-28°C | 26-28°C | 24-28°C |
| pH | 6.5-7.5 | 7.0-8.0 | 6.5-7.0 | 6.5-7.5 |
| Ammonia (NH3) | 0 ppm | 0 ppm | 0 ppm | 0 ppm |
| Nitrite (NO2) | 0 ppm | 0 ppm | 0 ppm | 0 ppm |
| Nitrate (NO3) | <40 ppm | <20 ppm | <20 ppm | <20 ppm |
| Hardness (GH) | 5-15 dGH | 10-20 dGH | 3-8 dGH | 5-15 dGH |
| Dissolved Oxygen | >6 mg/L | >5 mg/L | >5 mg/L | >4 mg/L |
Emergency Water Quality Correction
Problem: High Ammonia (>0.5 ppm)
- Immediate 50% water change
- Stop feeding for 24 hours
- Add ammonia detoxifier
- Increase aeration
- Check filter function
Problem: High Nitrite (>0.5 ppm)
- 30% water change
- Add aquarium salt (1g/L)
- Increase aeration
- Add beneficial bacteria
Problem: pH Crash (below 6.0)
- Gradual water change (20% every 2 hours)
- Add crushed coral/limestone
- Check for dead matter
- Increase aeration
Problem: Temperature Spike (above 32°C)
- Add ice bottles (in bags)
- Increase water circulation
- Reduce feeding
- Partial water change with cooler water
Appendix C: Common Disease Identification Chart
Common Diseases in Ornamental Fish
| Disease | Visual Symptoms | Behavioral Signs | Cause | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Spot (Ich) | White spots like salt grains | Rubbing against objects, rapid breathing | Parasite (temperature stress) | Raise temp to 30°C, add salt, medication for 7 days |
| Fin Rot | Ragged, discolored fins | Lethargy, fins clamped | Bacterial infection | Antibiotics, improve water quality |
| Dropsy | Swollen body, raised scales | Lethargy, loss of appetite | Bacterial, often terminal | Isolate, antibiotics (limited success) |
| Fungus | Cotton-like white growth | Rubbing, lethargy | Secondary to injury/stress | Antifungal medication, salt bath |
| Velvet | Gold dust appearance | Lethargy, gasping | Parasite | Darkness + medication for 5-7 days |
| Swim Bladder | Floating/sinking abnormally | Can’t maintain position | Overfeeding, constipation | Fast 3 days, feed peas, Epsom salt |
| Columnaris | White/gray patches, mouth rot | Lethargy, gasping | Bacterial | Antibiotics, improve conditions |
Appendix D: Monthly Expense Tracker Template
MONTHLY EXPENSE SHEET – [Month & Year]
Feed
| Date | Type | Quantity | Supplier | Amount | Bill No |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
Total Feed Expense: _______
Electricity
Meter Reading Start: ___ End: ___ Units: ___ Amount: ___
Labor
| Person | Days Worked | Rate | Amount | Signature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
Total Labor: _______
Chemicals/Medicines
| Date | Item | Purpose | Amount | Bill No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
Total: _______
Transport
| Date | Purpose | Distance | Fuel | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
Total: _______
Miscellaneous
| Date | Item | Amount | Bill No |
|---|---|---|---|
| ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
Total: _______
Loan EMI: _______
Insurance: _______
Rent (if applicable): _______
_______
Total Sales: _______
Other Income: _______
TOTAL INCOME: _______
_______
Prepared by: _______ Date: _______
Verified by: _______ Date: _______
Appendix E: Species-Wise Breeding Protocol
Goldfish Breeding Protocol
- Broodstock Selection
- Age: 2-3 years
- Size: 10-15 cm
- Ratio: 2 males : 1 female
- Conditioning: 2 weeks on protein-rich diet
- Breeding Setup
- Tank: 500-1000 liters
- Temperature: 20-24°C
- Spawning mop or plants
- Shallow water (20-30 cm)
- Spawning Process
- Trigger: Temperature rise + water change
- Time: Early morning
- Duration: 2-3 hours
- Eggs: 1000-2000 per female
- Post-Spawning
- Remove parents immediately
- Maintain temperature
- Aeration (gentle)
- Hatching: 3-5 days
- Fry Care
- First feed: Infusoria (day 5-7)
- Second week: Brine shrimp
- Third week: Micro pellets
- Marketable: 3-4 months
Appendix F: Business Plan Template
BUSINESS PLAN: ORNAMENTAL FISH REARING UNIT
Under PMMSY
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Business Name: _______________
Owner: _______________
Location: _______________
Project Cost: ₹8,00,000
Subsidy Expected: ₹_______
Own Investment: ₹_______
2. BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
Type: Medium Scale Ornamental Fish Rearing
Target Species: [List 5-7 species]
Target Market: [Delhi NCR/Local/Export]
Unique Selling Point: [Quality/Service/Variety]
3. MARKET ANALYSIS
Market Size: [Local demand assessment]
Competition: [Number of competitors, their strengths]
Your Advantage: [Location/Quality/Price/Service]
Growth Potential: [Market trends]
4. PRODUCTION PLAN
Year 1: _____ fish
Year 2: _____ fish
Year 3: _____ fish
Species Mix: [Percentages]
5. MARKETING STRATEGY
Primary Channel: _______________
Secondary Channel: _______________
Pricing Strategy: _______________
Promotional Plan: _______________
6. FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS
Revenue Year 1: ₹_______
Revenue Year 2: ₹_______
Revenue Year 3: ₹_______
Break-Even: Month _____
ROI: ____%
7. RISK ANALYSIS
- Risk 1: [e.g., Disease outbreak] – Mitigation: [Quarantine protocol]
- Risk 2: [e.g., Market price crash] – Mitigation: [Diversification]
- Risk 3: [e.g., Power failure] – Mitigation: [Backup system]
8. IMPLEMENTATION TIMELINE
- Month 1-3: Construction
- Month 4-6: Equipment installation
- Month 7-9: Stocking and initial production
- Month 10-12: First sales
9. TEAM
Owner: [Qualification, Experience]
Staff: [Number, Roles]
Consultants: [Technical, Financial]
10. APPENDICES
- Land documents
- Cost estimates
- Market research data
- Letters of intent from buyers
Disclaimer: This comprehensive guide is based on the PMMSY Operational Guidelines issued by the Department of Fisheries, Government of India in June 2020. While every effort has been made to provide accurate information, applicants should:
- Verify all details with their District Fisheries Office
- Check for latest updates and amendments to PMMSY
- Consult officially published guidelines before applying
- Understand that unit costs and terms may be revised
- Seek professional advice for legal and financial matters
The Government of India, Department of Fisheries reserves the right to modify any terms, conditions, or guidelines under PMMSY as deemed necessary. This guide is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or financial advice.
For Official Information:
- Visit: dof.gov.in
- Contact: Your District Fisheries Officer, Haryana
- NFDB Website: nfdb.gov.in
This guide concludes with best wishes for your entrepreneurial journey in ornamental fisheries. May your waters be clear, your fish healthy, and your business prosperous!
JAI HIND | JAI KISAN | JAI VIGYAN
FAQs
Who is eligible to apply under this scheme?
Residents of Haryana with a valid Parivar Pehchan Patra, owning or leasing at least 150 sq. meters of land with an adequate water facility, are eligible.
Can leased land be used for the project?
Yes, leased land is allowed if the applicant holds a registered lease deed valid for a minimum of 7 years.
What is the estimated project cost?
The estimated project cost is ₹8,00,000 per unit.
How much subsidy is available under this scheme?
SC/Women: 60% of project cost (₹4,80,000)
General Category: 40% of project cost (₹3,20,000)
What type of infrastructure is covered under the scheme?
Sheds, breeding units, rearing tanks, and culture tanks for ornamental fish farming are covered.
What documents are required for application?
Agreement letter, ID proof, caste certificate (if applicable), fisheries training certificate, land records/lease deed, DPR/SCP, bank account & PAN details, and project-related bills/vouchers.
Is fisheries training mandatory?
Yes, applicants must provide a Fisheries Training Certificate to ensure they have basic knowledge of ornamental fish farming.
Will there be a site inspection before approval?
Yes, the Fisheries Department conducts site inspections to verify land, water facilities, and feasibility before sanctioning.
What is the role of the Agreement Letter?
It is a formal agreement between the beneficiary and the Fisheries Department outlining scheme terms, responsibilities, and subsidy utilization.
Are bills and vouchers required?
Yes, proper bills, receipts, and vouchers must be submitted for expenses incurred under the project for subsidy release.
Can multiple units be set up by one beneficiary?
No, generally one unit is allowed per beneficiary to ensure wider coverage. However, expansion may be considered as per departmental guidelines.
How can an applicant apply for this scheme?
Applications can be submitted online through the Antyodaya-SARAL Portal or via Common Service Centres (CSCs).
What are the charges for applying?
Government Charges: ₹0
Service Charges: ₹10
Atal Seva Kendra Charges: ₹10
How can applicants track their application status?
Applicants can track via:
SMS by sending “SARAL <Application ID>” to 9954699899
Antyodaya-SARAL Portal (online tracking)